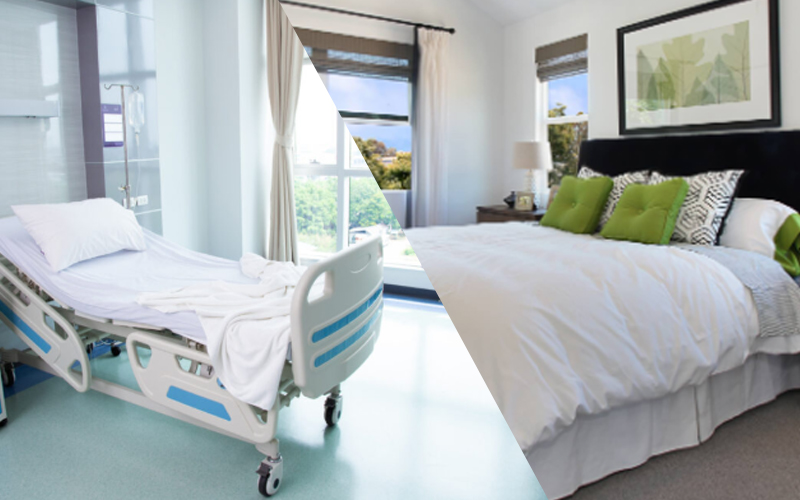
Definition Comparison
Medical beds and regular beds serve different purposes. Their design and features set them apart.
What Is a Medical Bed?
A medical bed is built for patient care. Here are the main features:
– Adjustable frames. You can change height and position for easier access and comfort.
– Special mattresses. These help relieve pressure and maintain hygiene.
– Built-in safety features like side rails. These prevent falls.
– Extra functions that help with medical treatment and caregiving.
What Is a Regular Bed?
A regular bed is made for everyday sleep and rest. It offers:
– A simple frame. It does not adjust.
– Standard mattresses. These focus on basic comfort, not medical support.
– Few or no safety features.

Adjustability Features
Medical beds offer advanced adjustability. This improves patient care. It also makes life easier for caregivers.
Head and Foot Elevation
Medical beds and some high-end adjustable beds let you raise or lower the head and foot sections.
I recommend these adjustments for people with sleep apnea, acid reflux, or leg swelling. They make getting in and out of bed simpler.
Height Adjustability
Vertical height adjustment is a major advantage of medical beds. The entire bed moves up or down. This makes transfers to wheelchairs or other equipment much safer.
Caregivers experience less physical strain during patient transfers. I’ve seen this reduce workplace injuries.
Most regular adjustable beds sit at one fixed height. They don’t offer this feature.
Precision and Range of Adjustments
Medical beds give you more precise controls. Some tilt into trendelenburg and reverse trendelenburg positions. This angles the entire bed surface for specific medical treatments.
You can turn the bed into a chair for difficult procedures. This provides easier access. Standard adjustable beds offer much less movement.
Safety and Emergency Features
Medical beds include side rails and emergency positioning options. These rails protect people who struggle with movement. They help prevent falls.
Regular beds don’t have rails. Even adjustable ones lack quick-release options for emergencies.
Medical Accessory Compatibility
Medical beds support professional care. You can attach over-bed tables, IV poles, and other devices without hassle.
Based on my experience, regular beds don’t work with these medical accessories. This limits their use for serious care needs.
Safety Features of Medical Beds vs. Regular Beds
Medical beds include advanced safety features. They protect vulnerable users and support clinical care. Regular beds don’t provide these features.
Integrated Safety Features in Medical Beds
Side Rails:
Medical beds offer adjustable side rails. You can choose quarter, half, or full length to prevent falls. Some have padding for extra protection. Most clinical settings require these. Regular beds seldom include side rails.
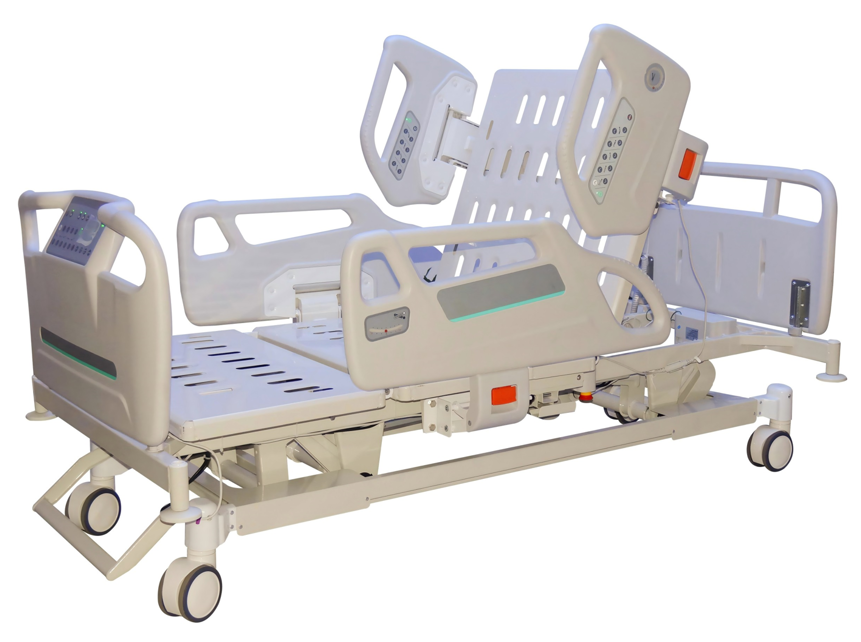
Bed Height Adjustment (Hi-Low):
Medical beds can be lowered (as low as 14–16 inches) or raised (up to 32–35 inches). You use powered or manual controls. This flexibility reduces fall risk during transfers. Caregivers can work without strain. Regular beds stay at a fixed height. They lack this essential function.
Bed Exit Alarms:
Built-in alarms detect when a patient tries to leave the bed. Caregivers get alerted right away. This lowers the chance of unattended falls. Clinical studies show advanced alarm systems can reduce falls by up to 55%. I recommend this feature for high-risk patients. Regular beds do not offer this.
Locking Mechanisms:
Hospital beds use locking casters. These keep the bed stable during transfers and treatments. Regular beds don’t have lockable wheels. This creates safety concerns during repositioning.
Ergonomic and Accessibility Enhancements:
Grippable handrails ease movement in and out of bed.
Slide guards and adaptable sections prevent slipping. They help with repositioning.
Easy-to-use controls—such as pendant remotes or pedal-adjustments—allow safe, quick changes. Patients or caregivers can operate them.
Features for Emergencies and Infection Control:
Battery backup systems keep beds working during power outages. This can be life-saving.
Antimicrobial materials and easy-to-clean surfaces promote hygiene. They help with infection control.
High Load Capacity:
Medical beds support 500–650 lbs. They accommodate bariatric users and medical equipment. Regular beds cannot handle such heavy loads. They are not reliable for these needs.
These integrated safety features make medical beds crucial for clinical environments. They help prevent injuries. They support patient care. I believe they offer peace of mind to both users and caregivers.
Durability and Materials
Medical beds are built to last. They handle tough environments. I’ve seen them withstand frequent moves, heavy use, and strong cleaning products. Regular beds can’t match this.
Lifespan and Material Construction
Medical beds last 10–15 years. Their frames are reinforced. Their parts are specialized.
Regular beds last 5–7 years with normal use.
Medical beds use high-density foam, gel, or air-based mattresses with waterproof, antimicrobial covers. These prevent bacteria and meet strict hygiene needs.
Regular beds use memory foam, traditional springs, and cotton fabrics. These feel comfortable but break down faster under pressure.

Cleaning and Hygiene
Medical beds handle cleaning every day or week without damage. Frames and covers resist harm from disinfectants and scrubbing.
Regular beds suffer from moisture and cleaning products. Most don’t have antimicrobial or waterproof features.
Maintenance and Longevity
Strict maintenance protocols extend medical bed life. Beds with good care last beyond 10–15 years, even with heavy use.
Appearance and Aesthetics of Medical Beds vs. Regular Beds
Medical beds and regular beds look very different. This reflects what each bed type is meant to do.
Visual Design and Materials
Medical beds have a clinical look. You will see metal frames, mechanical parts, and plastic or metal panels. Guardrails and wheels are always there. Safety and function matter more than style.
Most surfaces are antimicrobial and easy to clean. These beds handle frequent disinfection. Their finishes resist harsh cleaning products. But they don’t include decorative features.
The design feels functional. Sometimes it feels impersonal. Its goal is to support hygiene and patient care. This can make a room look more like a hospital.
Regular beds focus on home aesthetics. You will see wooden frames, upholstered headboards, and appealing trims. Decorative details and fabric coverings are common. They match other home furniture.

Materials like wood grain, leather, linen, or cushioned textiles create a cozy feel. The design blends with bedroom décor. It makes the space feel warm and welcoming.
These beds don’t feature mechanical parts or safety rails. Wheels or adaptive elements are custom additions, not standard.
Cost Comparison: Medical Beds vs. Regular Beds
Medical beds and regular beds have big price differences. This comes from their features and what they’re made for. Here’s how the costs break down:
Price Range Examples
Basic Manual Medical Bed (with standard medical mattress): $600–$1,200
Standard Twin Regular Bed (with foam mattress): $300–$800
Full Electric Bariatric Medical Bed (for home use): $3,000–$10,000
Luxury King-Size Regular Bed Set: $1,000–$3,000
Medical Bed vs. Regular Bed: Comparison Table
I recommend you compare these key features, sizes, functions, and costs of medical beds and regular beds side by side.
|
Feature |
Medical Bed |
Regular Bed |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard Size |
36″ x 80″ (91 cm x 203 cm). Other options: 39″ x 80″ (IV). Bariatric models: 42″–60″ wide, up to 221 cm long. |
Twin: 39″ x 75″ (96.5 cm x 190.5 cm). Full: 54″ x 75″. Queen: 60″ x 80″. King: 76″ x 80″. Cal King: 72″ x 84″. |
|
Height Range |
Adjustable from 7″ to 30″. This range covers Ultra Low to maximum height for safe transfers. |
Fixed at 18″–25″. |
|
Adjustability |
Head, foot, and bed height adjust on their own. Options include manual, semi-electric, or full-electric. Trendelenburg positions available. |
Fixed in most cases. Some bases offer limited head or foot tilt. |
|
Purpose/Use |
I suggest these for medical facilities, home care, rehab, fall prevention, and long-term clinical support. |
Built for homes or hotels. Designed for everyday sleep and rest. |
|
Material/Build |
Steel-reinforced frame. Antimicrobial finishes. Meets medical regulations. Handles repeated cleaning and high stress. |
Consumer-grade wood, steel, or upholstered frames for home use. |
|
Motor System |
Multiple electric motors control bed position and features. Bariatric beds use powerful motors. |
Premium “adjustable beds” may have motors. Most beds are manual or fixed. |
|
Cost Range |
Standard: $500–$3,000. Advanced or Bariatric: $2,000–$10,000+. Insurance often covers part or all cost. Rentals available. |
Typical household bed: $200–$2,500. Out-of-pocket purchase. No insurance coverage. |
|
Extra Features |
Side rails, IV pole ports, emergency CPR release, bed exit alarms, fall alarms, lockable wheels, pressure-relief mattresses, infection control features. |
Medical accessories are rare. Safety features uncommon. Focus is on style. |
