What are the main hospital bed parts?
What makes a hospital bed safe and reliable? Many people think it’s just a metal frame with a mattress. I’ve learned that a modern hospital bed is far more complex. It’s a sophisticated piece of medical equipment. Eight critical components work together to ensure safety.
Take the load-bearing frame, for example. It supports up to 550 pounds. Then there are the silent German motors. They enable precise positioning for patient comfort. Each part plays a vital role in patient care. Each part aids in recovery.
The following are the key parts of a hospital bed:
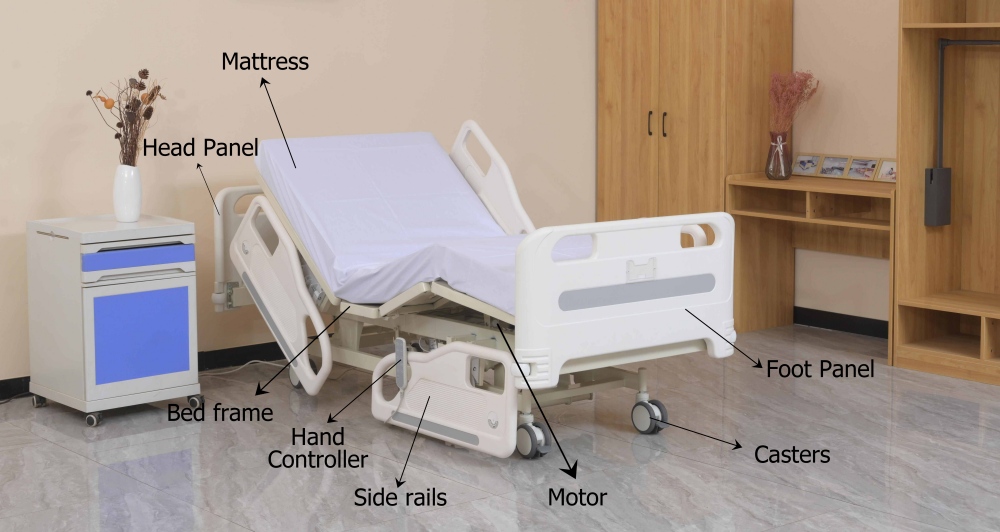

Bed Frame
The hospital bed frame forms the core structure of any hospital patient bed. It supports the patient and all other hospital bed parts. Its design and quality matter most for stability, durability, and patient safety.
Material Construction and Properties
Hospital bed frames are built from high-strength steel or aluminum alloy.
Steel hospital bed frames offer more weight and stability. They are well-suited for high-dependency environments.
Aluminum frames weigh less. They improve bed mobility and make repositioning easier.
Most frames use cold-rolled steel tube construction. This ensures excellent load-bearing capacity. Coatings protect the hospital bed frame from corrosion for long-term hospital use.

Advanced Adjustment Capabilities
Modern hospital bed frames feature electric lifting mechanisms. These adjust height to suit clinical procedures.
Multi-angle positioning of head, waist, and feet is standard.
Five-function electric hospital beds control height, backrest, knee-rest, and both Trendelenburg and reverse Trendelenburg positioning.
Premium frames may feature lateral tilt and five-motor drive systems for full adjustability.
Safety and Quality Engineering
All joints and welds in the frame undergo strict quality checks. This prevents breakage or deformation. The design focuses on impact and vibration resistance. It maintains stability during emergencies.
Frames support up to 250kg in patient weight.
Some strong models weigh 170 lbs for the frame alone, showing their strength.
Platform Construction Details
The sleeping platform uses a four-section modular design. It features cold-rolled steel stamping.
Ventilation holes allow for optimal airflow and reduce moisture buildup.
An electronic epoxy coating finishes the surface. This adds durability and infection control.
The perforated platform ensures patient comfort and meets hygiene standards.
All hospital bed parts, including platforms, are designed for long service life. When replacement is needed, reliable hospital furniture spare parts help maintain performance and safety.
Mattress
The medical mattress is one of the most important parts of a hospital bed, directly affecting patient comfort and medical outcomes. This is especially critical for immobile patients or those at risk of pressure injuries.
Hospital Bed Mattress Types and Clinical Features
Weight Capacity: Standard mattresses for a patient bed support 350–550 lbs.
Types of Hospital Mattresses:
Innerspring, Foam, Memory Foam, Air (Dynamic/Low Air Loss), and Hybrid/Pressure Redistribution models are available.
Surface Covers and Hygiene:
Waterproof and antimicrobial covers help prevent infections and maintain cleanliness.
All mattresses used in a patient bed are easy to clean, supporting quick turnover.
Flame retardancy meets medical safety regulations.
Pressure Injury Prevention and Compliance
Pressure Redistribution: This feature lowers the risk of pressure ulcers, benefiting long-term and immobile patients. In practice, air and memory foam mattresses perform well clinically.
Hygiene and Safety Standards:
Flame resistance allows use in high-risk settings.
Waterproof coatings simplify decontamination and support infection control.
Like other hospital bed parts, mattresses are designed for durability and safety. Should replacement be needed, hospital furniturespare parts, including mattress covers and internal components, help maintain the parts of bed performance and hygiene.
Side Rails
Side rails are essential parts of a hospital bed, designed to keep patients safe. They are particularly useful for those with limited mobility or fall risk. These rails create protective barriers on both sides of the bed and assist patients with repositioning and movement.
Types of Hospital Bed Side Rails
ABS Four-Small Guardrail (Damping Lift): Compact and easy to adjust, this guardrail is user-friendly and reliable.
ABS Large Guardrail (Damping Lift): Offers greater coverage and stability, recommended for high-risk patients.
Aluminum Alloy/Stainless Steel Foldable Guardrail: Available in five or six-position designs, it is highly adjustable and can be folded down for easy access.
Full-Length Guardrail: Provides maximum fall prevention along the entire bed length.
Half-Length and Quarter-Length Guardrails: Offer partial coverage while maintaining safety and facilitating patient entry and exit.
Most side rails can be raised or lowered and synchronize with electric bed adjustments. Spring-loaded releases allow for smooth and simple operation.
Materials and Customization Options
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Used in blow-molded or injection-molded rails, it is impact-resistant, durable, and easy to clean.
Aluminum Alloy/Stainless Steel: Ideal for multi-bar designs, combining strength with lighter weight.
Customization: Hospital bed factory such as Grace Medy offer custom sizes, including taller or special-dimension rails, to meet specific clinical needs. These options are often listed in a hospital bed parts catalog.
Patient Safety Impact
Side rails are highly effective for high-fall-risk patients, such as the elderly or those with balance issues. Research shows a significant reduction in falls and injuries when these parts of a hospital bed are correctly selected and used. Proper integration with other parts of a bed frame ensures overall safety and support.
Casters: Hospital Bed Wheels for Mobility and Safety
Hospital bed casters are essential parts of a hospital bed, providing smooth mobility, secure positioning, and dependable performance in clinical environments.
Hospital Bed Caster Size and Load Capacity
Common wheel diameters include 100 mm, 125 mm, 150 mm, and 200 mm (or 3″, 4″, 5″, 6″, and 8″ equivalents).
Each caster typically supports at least 90 kg (198 lbs), with heavy-duty models handling over 300 kg (660 lbs) per wheel.
This robust design allows the bed frame hospital to move safely with patients and any attached medical equipment.
Material Quality and Durability
Casters are made from high-quality materials such as:
Polyurethane or rubber treads for quiet, smooth rolling and shock absorption.
Steel or die-cast aluminum for the frame and fork, ensuring strength and longevity.
Polyamide (nylon) or thermoplastic for lighter models with corrosion resistance.
Some premium casters feature dual-wheel designs or reinforced nylon for enhanced stability.
Steel or aluminum-body casters are recommended for high-traffic areas such as the ICU, where durability among parts of the hospital bed is critical.
Hospital Bed Wheel Braking and Locking Systems
Central locking allows all wheels to be secured with one pedal, important during patient transfers or emergencies.
Total lock and directional lock functions prevent bed movement or limit it to a straight path, reducing drift.
These features help keep the bed structure name and its components securely in place, even on sloped or busy ward floors.
Performance, Comfort, and Hygiene
Shock-absorbing designs with soft rubber or pneumatic tires reduce vibration and noise, increasing patient comfort.
High-grade bearings and rubber treads enable quiet operation.
Antistatic (ESD) casters protect medical electronics and support infection control through washable designs.
Investing in casters with advanced braking and ESD features is recommended for ward safety and flexibility. Well-designed casters contribute to the overall function of parts of a bed, improving both patient care and staff efficiency.
Control System (Hand Controllers)
Hand controllers are the core of the control system for an adjustable hospital patient bed. These electronic units allow patients and caregivers to operate the bed easily, enhancing comfort, care, and safety.
Key Technical Features and Specifications
Modern hand controllers are user-friendly and versatile:
Electric actuation allows smooth, quiet adjustment of the hospital bed frames, including raising or lowering the bed, as well as moving the backrest and footrest.
Multi-row, multi-button layouts—such as the Grace Medy model with up to 12 buttons, 6 rows, and LED indicators—support clear operation.
LED status indicators show which functions are active or locked.
Security systems with magnet sensors and electronic locks prevent unauthorized use.
Quick-release functions allow emergency staff to quickly flatten the bed or change its position.
Use Cases and Value in Clinical Settings
Hand controllers are commonly used in:
ICU and acute care beds, where frequent repositioning is necessary
Bariatric beds, which support higher weight limits
Long-term care, promoting patient independence and reducing staff workload
For example, learning how to lower hospital bed height or adjust sections is simple with an intuitive hand controller.
Based on experience, it is recommended to choose durable, feature-rich controllers. Models with more buttons, backlighting, and quick-release functions are ideal for high-dependency wards or immobile patients. Waterproof and impact-resistant designs help maintain performance and hygiene during daily use in any hospital patient bed.
Foot and Head Panels
Foot and head panels are essential hospital bed parts that provide structural support and functional utility. Typically made from ABS or PP plastic, these panels offer high strength, durability, impact resistance, and easy cleaning—features I highly recommend for busy hospital environments.
Functional Features and Safety Design
Mattress Retention and Patient Stability:
The panels prevent the mattress from shifting at either end, keeping it properly positioned on the hospital bed frame. This enhances patient stability during movement or bed adjustment.
Usage Environments
These hospital bed parts are commonly used in ICUs, inpatient wards, private recovery rooms, and neonatal units.
Hospitals can also request custom panel features to meet specific clinical needs, supporting both medical workflows and patient comfort as part of a complete hospital bed frame system.
Motors (for Electric Beds)
Electric hospital beds rely on robust motors for precise positioning. These motors enable smooth, automated bed adjustment and are essential for modern patient care, supporting frequent use across varying patient loads.
Hospital Bed Motor Types and Engineering
German-made motors are widely used in semi-electric and full-electric beds, setting a benchmark for durability and quiet operation.
Engineered for heavy-duty, continuous use, motors undergo strict lifecycle testing—hand controls are often validated over 500,000 cycles.
Many models feature welded steel split frames that integrate with motor units, improving stability even at full capacity.
Emergency Backup and Safety Systems
Battery emergency backup:
Integrated 9V battery systems allow safe lowering of the head and foot sections during power loss.
Manual override:
Ensures basic adjustments remain possible during motor service or blackouts.
These features help maintain safety and support hospital emergency protocols.
Performance, Reliability, and Value
Motors are built for long-term, quiet, and smooth performance under high loads.
German or equivalent-grade motors are recommended for reliability in clinical environments.
Proven lifecycle testing and stable design reduce long-term maintenance needs. Having key hospital furniture spare parts such as replacement motors on hand further minimizes bed downtime, offering greater value for high-use wards and critical care units.
After years in healthcare, I’ve come to realize that understanding these components isn’t just technical knowledge—it’s about appreciating how each part works together to protect someone’s loved one. Whether you’re a caregiver, facility manager, or family member, knowing what makes a hospital bed truly functional empowers you to make better decisions. Quality doesn’t happen by accident; it’s built into every motor, rail, and caster. And that quality directly translates into safer recoveries and greater peace of mind for everyone involved.
